Many people – corporate decision-makers in particular – hope that this 2022 moves forward under the “back to normal” banner. Rising vaccination rates, some professionalization in the personal and societal handling of the new situation of a long-lasting COVID-19 pandemic, and digital technologies allow this hope to seem quite realistic. In the meantime, it is no real news to label the last two years spent through and with the pandemic as “exceptional”.
Yet 2022 is once again a very decisive year for companies, for it will set the course for the future. It will also show how companies can handle with a cool head the sudden increase in relevance and competitive intensity in digitalization. After two years of radical change in many areas of life, is there really a “normal – as before” or will the new “normal” look somewhat different?
Companies have clearly stepped up the pace. They’ve used the last year to make a leap in time to 2030 in terms of digitalization (see our Tech Tends 2021 article). For example, the digital workplace is no longer a project of the future. Digital customer interaction channels have also become the new standard. Not all activities that were pushed forward in 2020 and 2021 are already operational today. Companies always have work ahead of them – whether to maintain and continuously improve those initiatives that have been launched or to finally go live and be able to use them this year. However, real digital business is still often a marginal activity for companies. In most cases, the good and promising projects for monetizing data and digital services are still pilots or sub-portfolios. However, they have successfully put the technical feasibility, customer acceptance and the company’s ability to deliver to the test. As a result, they are on the verge of breakthrough in many places – but also of failure.
In the process, not only business and IT are inevitably growing closer together, but often all parts of the company. For example, the boundaries of traditional office IT are blurring with production IT and the entire supply chain, all the way to digital sales and aftersales. At the same time, users are not content with the new status quo, but are raising their standards even higher. The result is individualization or mass customization. Consumption in abundance, but at the same time services tailored individually to each person and situation represent the new expectations.
It is therefore clear that digitization will not yet be a feel-good topic for companies in 2022. Those that successfully transition from the chaos and speed phase to a scaling phase will be on top.
Business Models, Trust in Technology and Innovations on the Horizon Shape Technology & Digital Trends 2022
Corporate decision-makers want to take the momentum of recent years in terms of digitalization into the new year. They now have the chance to use the newly discovered opportunities in a sustainable and efficient way. With this year, decisions can once again be made with a slightly more long-term orientation, which minimizes risk but also increases expectations of success.
For digital and IT leaders, this means that their initiatives will now be evaluated more critically (again). This stage is a great opportunity, but it is also a burden. After all, it is not only a matter of successfully placing the business opportunities on the market as software and services but also of successfully exploiting the synergies at the technological level.
Last but not least, the focus should also be sharpened beyond the current year so that, particularly in the German-speaking and Central European region, new innovations in technology do not become a competitive and existential threat to SMEs. The opportunity is there to build up a buffer for innovation budgets, which are then used precisely for this purpose and have an impact beyond the actual core business.
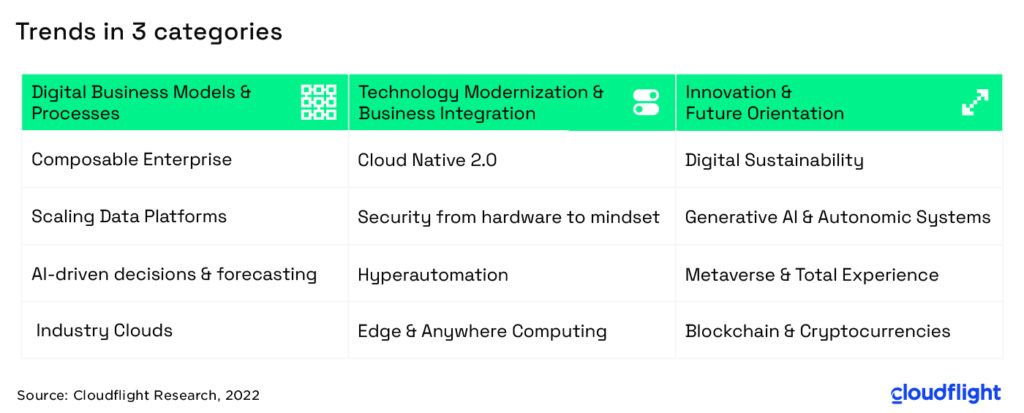
Thus, the technology and digitalization efforts of companies should be dedicated primarily to the following three areas:
- Digital Business Models & Processes: Identifying and, most importantly, completing the right initiatives for a successful Digital Marketplace.
- Technology Modernization & Business Integration: Creating and maintaining a successful and trustworthy IT landscape in all areas.
- Innovation & Future Orientation: Anticipating the coming generation of digital innovations and making them usable for oneself early on
Digital Business Models & Processes
Composable Enterprise establishes itself as a basic principle of digitalization
Digitalization has always affected all areas of the company. Over time, this understanding has also become more firmly established among decision-makers. At the same time, many successful projects and initiatives still depend on the core applications and the long-established processes, business logics and applications. These must be accessible by numerous new applications and services, and in some cases must even be able to be changed in real time. But before companies go to the trouble of mirroring and completely replacing their back-end logics, APIs and abstraction layers help to ensure that data and microservices are available everywhere and, at the same time, that traditional systems can withstand these demands.
In the “Composable Enterprise” approach, companies can respond dynamically to market changes and new demands on their IT architecture by combining applications and operating them as non-exclusive packages. For example, production IT and customer service can access the same backend without having to develop and deploy two technically independent worlds. The composable approach has some technical implications but is also significant for dynamism and responsiveness at the strategic and organizational level.
Data platforms go live in 2022
The first operational implementations of the Composable Enterprise are data and development platforms that numerous companies are currently building. As a new abstraction layer between traditional back-end IT and data silos and the new (micro) services for digital business processes, models or customer interaction channels, they will be of great importance in the future.
In the vision of these data platforms, all data streams run over or through a virtual platform. With this integration, companies gain tremendous speed and save high investments for fundamental modernization projects. Data from a wide variety of business units is made available to the same or other business units and can even make changes to the core system as needed. This still means a lot of work for many companies when it comes to building, maintaining and governance and especially the new business applications on top of it. However, many companies will go live with their platforms this year and will be able to gain initial experience and monetary success.
AI-driven decision-making and forecasting creates competitive advantage
Artificial Intelligence and algorithms have been playing a major role for some time now – especially in the media. Nevertheless, numerous companies have proven that the intelligent linking of large amounts of data can create a significant competitive advantage because, although algorithms are not the real world, they can now represent it well. Provided the data entered is quantitatively and qualitatively sufficient, even complex business logics can be represented and provide significantly better planning and decision-making for the C-level. The new league of AI-based decision-making and forecasting, even for operational areas, goes beyond the capabilities of classic BI systems.
With increasingly complex logics, while visualization is becoming easier for users to consume, the logic behind it is becoming more complex and individualized. Companies need data scientists and business experts to work together to identify and create those logics that are currently causing inefficiencies and uncertainties in the company. Overcoming this will become increasingly possible this year.
Industry Clouds gain new fame
Industry-specific community clouds, which have functioned as associations of companies in more or less homogeneous business areas, are not a new concept per se. Communities of interest were already formed a few years ago, which mostly took this route for cost reasons. The large cloud providers have also brought more and more industry-specific solutions onto the market in recent years, but these were usually nothing more than the compilation of already existing services with a few functional add-ons.
This year, however, the demand for industry clouds and standardized solutions for specific areas of application will grow again, primarily due to the increasing requirements outlined earlier. In fact, even in the GAIA-X environment, there are some approaches, such as Catena-X, that go exactly in this direction. Hyperscalers, industry software providers, but also user communities among themselves are all becoming the drivers here.
Technology Modernization & Business Integration
Cloud Native 2.0 shapes enterprise architectures
The basic acceptance of Cloud Computing has now been consolidated, but interpretation of its use still diverges. While technology and service providers tout a networked and customized landscape of infrastructure, containers, platform services and APIs, many enterprises have too often preferred a rehosting or overly conservative approach. The result has often been higher costs and few real benefits.
More and more, however, there is a growing realization that careful and deliberate vendor lock-in, targeted use of the right open-source tools, and thus the platform approach holds manageable risk and great potential. So, this year, enterprises will also move more towards using the full breadth of cloud platforms and deploy services in a targeted way to overcome the skills gap and use managed services, create new technical opportunities for the applications that are too expensive in traditional hosting and pure do-it-yourself, and thus gain experience of which of the perceived thousands of platform services are relevant for business use.
Security in transition from hardware appliances to mindset and AI
Decision-makers in this country have often distinguished themselves by having a good risk assessment and thus being more likely to protect against harm. With the growing number of services and data that also have business-critical significance for the company, “doing nothing” is now no longer an option. At the same time, traditional and sometimes static security measures, especially via traditional hardware appliances, are also reaching their limits. Finally, the shortage of chips and semiconductors is causing additional bottlenecks. Thus, in addition to firewalls and the like, which are still firmly established, there will have to be new approaches to cybersecurity and data security.
Many companies are thus starting first and foremost with the people themselves. With zero-trust concepts, DevSecOps, Security & Privacy by Design, and, finally, intensive employee training, data security should already be structurally granted. This gives companies the space to ensure security not only reactively, but also proactively.
Added to this are the AI tools and algorithms described above, which thereby bring software and service-side security to companies and use artificial intelligence to prevent major data leaks or downtimes from occurring in the company.
Hyperautomation from the business to the core areas of IT
Manual activities can no longer cope with the new volume and dynamics of digital services and business processes. To truly prepare companies for the next era of digitalization and ensure scalability, automation must become part of the strategy to an excessive degree.
Employees must be equipped with the appropriate tools and capabilities to automate manual, repetitive tasks easily and independently. Paper processes will soon be eliminated in public administration as well; we are already seeing the first offshoots and they will intensify in 2022.
Automation solutions will shape the administration of the architecture in management and IT, not least to ensure cybersecurity and uptime. Companies should therefore create the framework for how automation solutions nip inefficiencies in the bud in all areas and create free space for value-creating work.
Edge technologies confirm the trend toward Anywhere Computing
The networking of machines, devices and people under the collective term of the Internet of Things is just beginning. The offshoots already visible today in the professional environment, on the street or in the hand of every user with his smartphone show that the relevance of real-time data processing and digital services at the “edge” will work and be necessary.
Even in 2022, almost no new car or machine will be put into service that has standalone computing power. Technically, vendors have already positioned themselves in terms of Edge Computing. This is even largely true for the very critically regarded 5G network in Germany. Now it is up to the companies to successfully deploy these edge solutions and fill them with life, which once again entails new technical complexity that will pay off.
Innovation & Future Orientation
Digital sustainability beyond greenwashing
At the same time, the view into the future of digital technologies is also somewhat pathetically directed toward the future of the entire (surrounding) world. Many already expect that the wave of digitalization of business processes will be followed by the digitalization of the environment. What mankind is currently still taking from the environment in terms of technology, development and industry, it will very soon have to give back to an above-average extent.
Corporate sustainability efforts must therefore go beyond the current level of responsible stewardship of the environment and climate change. Developments for synthetic e-fuels, new energy generation, electromobility and the like are already in full swing. The same will also be the case very soon directly through technology.
Companies will not only see Digital Sustainability as a program for responsibility and marketing but will have to make it an integral part of their business strategies. This means that companies should already be developing a strategy for how they can reconcile progress, sustainability and competition and not have to pay dearly at some point for compensating for their current actions.
Digital Sustainability will be much more tangible and supported by technology this year. Initially, technology providers and large corporations will lead the way, but by the end of the year, all companies will be affected.
Generative AI & Autonomic Systems are being driven forward
Concerns about evil robots and Artificial Intelligence posing a threat to humanity persist. And these theories are getting new fodder from new breakthroughs in generative AI and autonomic systems. However, these breakthroughs are not so much the breeding ground for doomsday theories, but rather the logical next step in artificial intelligence and automation of business processes.
Generative AI allows algorithms to develop new (virtual) objects, such as images, text, or other files, that depend solely on context but did not exist before. For example, text descriptions can be used to generate images of people that do not exist in this way. Companies will find numerous use cases here that can make smart use of these capabilities. The same applies to autonomic systems. This describes systems that can make business decisions independently and put them into practice. Thus, decision-making mechanisms and controls, especially in industry, are becoming even more automated than before.
Generative AI and Autonomic Systems are currently relatively uncommon. However, the technical feasibility is largely there, so 2022 will be used primarily for finding and trying out the use cases.
Metaverse takes user experience to a new level
Now that companies have an overview of all previous digital channels to their internal and external users and can largely play them, the next trend is already on the horizon. After Facebook’s big announcement in the Metaverse and the renaming of the company to Meta, little has happened so far. But the fact that virtual and augmented realities play a major role in everyday life and user experience still doesn’t seem entirely far-fetched.
Many use cases are already emerging, particularly in medicine, research and development, but also in the global maintenance of machines. If the reach of augmented realities migrates into the metaverse in the coming years, even for everyday processes, companies will have to map a completely new user experience. Already today, the first offshoots and walking attempts across familiar devices and communication channels are conceivable. By 2022, the metaverse will be part of the new, all-encompassing user experience for employees, partners, and customers, at least in its initial stages.
Blockchain and cryptocurrencies set for 2nd attempt
Hardly any topic remains as controversial as blockchain and the megatrend around cryptocurrencies. With NFTs, a whole new speculation and investment trend is just germinating, which could already overcome the first critical hurdles. Still, many blockchains and cryptocurrencies currently in use remain very inefficient and are, in effect, the countermovement to Digital Sustainability.
However, it is usually not the pioneer use cases that ensure long-term success, but rather the second or third wave of use cases.
This could soon be the case with blockchain. This is because the developments around the technologies are immense and are receiving strong financial and content support. If smart contracts and currencies can be more efficiently and better integrated into the global business cycle, and at the same time the funds used do not exceed the benefits, we will soon see many success stories of cryptocurrencies and blockchains in real business use – even outside the financial world.
Another driver is the topic of web3 (also Web 3.0) which is currently taking shape and is set to revolutionize the World Wide Web. Here the role of blockchain is to establish a layer of trust to develop the web away from the big companies – towards a more independent platform to which everyone can contribute.